Overview

Your foot arch is your natural shock absorption system. Nature designed it so that when you put your body weight over your feet the shock is absorbed by this mechanism in order to alleviate the impact (and subsequent injuries) that would otherwise hit your feet, ankles, knees and hips. A flat foot is the most visible sign of overpronation, meaning that your arch collapses during the impact on the ground. As a consequence, your ankle twists inward and your knees overcompensates. Flat feet are a particular concern for runners, as during the running gait the arch is supposed to support on average 3 times their body weight.
Causes
Flat feet in adults can arise from a variety of causes. Here are the most common. An abnormality that is present from birth, stretched or torn tendons, damage or inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon (PTT), which connects from your lower leg, along your ankle, to the middle of the arch, broken or dislocated bones. Some health conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Nerve problems. Other factors that can increase your risk include obesity, diabetes, ageing and Pregnancy.
Symptoms
Arches can be seen as ?rolling downward? or collapsing when walking. Pain may present in lower back, hips or knees. Pain may be present on the bottom of the heels, within the arch, within the ankles or even the forefoot. Swelling can occur. Pain may occur in the anterior leg muscles.
Diagnosis
An examination of the foot is enough for the health care provider to diagnose flat foot. However, the cause must be determined. If an arch develops when the patient stands on his or her toes, the flat foot is called flexible and no treatment or further work-up is necessary. If there is pain associated with the foot or if the arch does not develop with toe-standing, x-rays are necessary. If a tarsal coalition is suspected, a CT scan is often ordered. If a posterior tibial tendon injury is suspected, your health care provider may recommend an MRI.
Can you fix a fallen arch?
Non Surgical Treatment
What we want to do is support the arch and maintain it in that curved position. So what you want is to bring the foot into a position where you hold and support the arch so you can get that correct heel-midfoot-big toe contact. You would achieve that with a level of arch support. People will take different levels of support, if you?re somebody who has movement in your arch, a strong level of support will hold and maintain you whereas if you?re someone whose arch has collapsed it could need more support and a level of correction built into the support to realign you. If you think of it, when your arch drops, it affects your foot but it also has a biomechanical effect on the rest of the body. But nothing that can?t be solved.
Surgical Treatment

A combination of surgical procedures can be used to reconstruct the flatfoot. Generally, these procedures can be separated into those that correct deformities of the bones and those that repair ligaments and tendons. Your orthopaedic surgeon will choose the proper combination of procedures for your foot. Surgery of the foot can be performed under regional anesthesia, which is numbing the foot and ankle with a nerve or spinal block, or general anesthesia, which may require a breathing tube. A nerve block is often placed behind the knee to reduce pain after surgery.
Prevention
Going barefoot, particularly over terrain such as a beach where muscles are given a good workout, is good for all but the most extremely flatfooted, or those with certain related conditions such as plantar fasciitis. Ligament laxity is also among the factors known to be associated with flat feet. One medical study in India with a large sample size of children who had grown up wearing shoes and others going barefoot found that the longitudinal arches of the bare footers were generally strongest and highest as a group, and that flat feet were less common in children who had grown up wearing sandals or slippers than among those who had worn closed-toe shoes. Focusing on the influence of footwear on the prevalence of pes planus, the cross-sectional study performed on children noted that wearing shoes throughout early childhood can be detrimental to the development of a normal or a high medial longitudinal arch. The vulnerability for flat foot among shoe-wearing children increases if the child has an associated ligament laxity condition. The results of the study suggest that children be encouraged to play barefooted on various surfaces of terrain and that slippers and sandals are less harmful compared to closed-toe shoes. It appeared that closed-toe shoes greatly inhibited the development of the arch of the foot more so than slippers or sandals. This conclusion may be a result of the notion that intrinsic muscle activity of the arch is required to prevent slippers and sandals from falling off the child?s foot.

Your foot arch is your natural shock absorption system. Nature designed it so that when you put your body weight over your feet the shock is absorbed by this mechanism in order to alleviate the impact (and subsequent injuries) that would otherwise hit your feet, ankles, knees and hips. A flat foot is the most visible sign of overpronation, meaning that your arch collapses during the impact on the ground. As a consequence, your ankle twists inward and your knees overcompensates. Flat feet are a particular concern for runners, as during the running gait the arch is supposed to support on average 3 times their body weight.
Causes
Flat feet in adults can arise from a variety of causes. Here are the most common. An abnormality that is present from birth, stretched or torn tendons, damage or inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon (PTT), which connects from your lower leg, along your ankle, to the middle of the arch, broken or dislocated bones. Some health conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Nerve problems. Other factors that can increase your risk include obesity, diabetes, ageing and Pregnancy.
Symptoms
Arches can be seen as ?rolling downward? or collapsing when walking. Pain may present in lower back, hips or knees. Pain may be present on the bottom of the heels, within the arch, within the ankles or even the forefoot. Swelling can occur. Pain may occur in the anterior leg muscles.
Diagnosis
An examination of the foot is enough for the health care provider to diagnose flat foot. However, the cause must be determined. If an arch develops when the patient stands on his or her toes, the flat foot is called flexible and no treatment or further work-up is necessary. If there is pain associated with the foot or if the arch does not develop with toe-standing, x-rays are necessary. If a tarsal coalition is suspected, a CT scan is often ordered. If a posterior tibial tendon injury is suspected, your health care provider may recommend an MRI.
Can you fix a fallen arch?
Non Surgical Treatment
What we want to do is support the arch and maintain it in that curved position. So what you want is to bring the foot into a position where you hold and support the arch so you can get that correct heel-midfoot-big toe contact. You would achieve that with a level of arch support. People will take different levels of support, if you?re somebody who has movement in your arch, a strong level of support will hold and maintain you whereas if you?re someone whose arch has collapsed it could need more support and a level of correction built into the support to realign you. If you think of it, when your arch drops, it affects your foot but it also has a biomechanical effect on the rest of the body. But nothing that can?t be solved.
Surgical Treatment

A combination of surgical procedures can be used to reconstruct the flatfoot. Generally, these procedures can be separated into those that correct deformities of the bones and those that repair ligaments and tendons. Your orthopaedic surgeon will choose the proper combination of procedures for your foot. Surgery of the foot can be performed under regional anesthesia, which is numbing the foot and ankle with a nerve or spinal block, or general anesthesia, which may require a breathing tube. A nerve block is often placed behind the knee to reduce pain after surgery.
Prevention
Going barefoot, particularly over terrain such as a beach where muscles are given a good workout, is good for all but the most extremely flatfooted, or those with certain related conditions such as plantar fasciitis. Ligament laxity is also among the factors known to be associated with flat feet. One medical study in India with a large sample size of children who had grown up wearing shoes and others going barefoot found that the longitudinal arches of the bare footers were generally strongest and highest as a group, and that flat feet were less common in children who had grown up wearing sandals or slippers than among those who had worn closed-toe shoes. Focusing on the influence of footwear on the prevalence of pes planus, the cross-sectional study performed on children noted that wearing shoes throughout early childhood can be detrimental to the development of a normal or a high medial longitudinal arch. The vulnerability for flat foot among shoe-wearing children increases if the child has an associated ligament laxity condition. The results of the study suggest that children be encouraged to play barefooted on various surfaces of terrain and that slippers and sandals are less harmful compared to closed-toe shoes. It appeared that closed-toe shoes greatly inhibited the development of the arch of the foot more so than slippers or sandals. This conclusion may be a result of the notion that intrinsic muscle activity of the arch is required to prevent slippers and sandals from falling off the child?s foot.





 A Morton's neuroma is a benign (noncancerous) swelling along a nerve in the foot that carries sensations from the toes. The reason the nerve starts to swell is unknown. But once swelling begins, the nearby bones and ligaments put pressure on the nerve, causing more irritation and inflammation. This produces burning pain, numbness, tingling and other abnormal sensations in the toes. A Morton's neuroma also is called an interdigital neuroma, intermetatarsal neuroma or a forefoot neuroma.
A Morton's neuroma is a benign (noncancerous) swelling along a nerve in the foot that carries sensations from the toes. The reason the nerve starts to swell is unknown. But once swelling begins, the nearby bones and ligaments put pressure on the nerve, causing more irritation and inflammation. This produces burning pain, numbness, tingling and other abnormal sensations in the toes. A Morton's neuroma also is called an interdigital neuroma, intermetatarsal neuroma or a forefoot neuroma.




 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms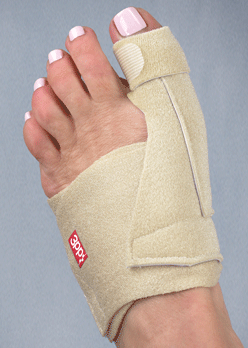 Knowing how bunions develop is helpful in selecting the appropriate bunion treatment. In general, most bunion deformities are a result of foot structure and function which are genetic. As the heel strikes the ground when walking, the joints of the foot unlock and absorb impact. Referred to as pronation, the arch collapses causing the feet to flatten. This flattening causes excessive tension of the tendon in the upper mid-foot that enables the big toe to bend upward. The tendon contracts which then forces the big toe to be pulled laterally toward the second toe. It can take many years for a bunion to develop, and especially to the point of pain. One can have a bunion but not yet experience any bunion pain. Conversely, one can suffer from bunion pain without having a severe deformity.
Knowing how bunions develop is helpful in selecting the appropriate bunion treatment. In general, most bunion deformities are a result of foot structure and function which are genetic. As the heel strikes the ground when walking, the joints of the foot unlock and absorb impact. Referred to as pronation, the arch collapses causing the feet to flatten. This flattening causes excessive tension of the tendon in the upper mid-foot that enables the big toe to bend upward. The tendon contracts which then forces the big toe to be pulled laterally toward the second toe. It can take many years for a bunion to develop, and especially to the point of pain. One can have a bunion but not yet experience any bunion pain. Conversely, one can suffer from bunion pain without having a severe deformity.
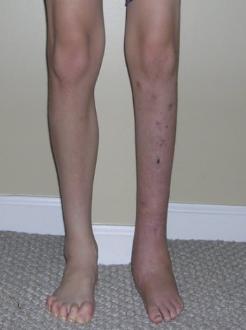
 An Achilles tendon injury can affect both professional and amateur athletes. The Achilles tendon is one of the longer tendons in your body, stretching from the bones of your heel to your calf muscles. You can feel it, a springy band of tissue at the back of your ankle and above your heel. It allows you to extend your foot and point your toes to the floor. Unfortunately, it's a commonly injured tendon. Many Achilles tendon injuries are caused by tendinitis, in which the tendon becomes swollen and painful. In a severe Achilles tendon injury, too much force on the tendon can cause it to tear partially or rupture completely.
An Achilles tendon injury can affect both professional and amateur athletes. The Achilles tendon is one of the longer tendons in your body, stretching from the bones of your heel to your calf muscles. You can feel it, a springy band of tissue at the back of your ankle and above your heel. It allows you to extend your foot and point your toes to the floor. Unfortunately, it's a commonly injured tendon. Many Achilles tendon injuries are caused by tendinitis, in which the tendon becomes swollen and painful. In a severe Achilles tendon injury, too much force on the tendon can cause it to tear partially or rupture completely.
